Have a question? 06 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🔥 It's our anniversary: 30% off with the code 7YEARS!!! 🥳 ( excluding accessories and gummies)
Have a question? 06 70 73 89 02

Think you know everything there is to know about CBD? It's not all that certain. Here are five truly astonishing facts about cannabidiol.
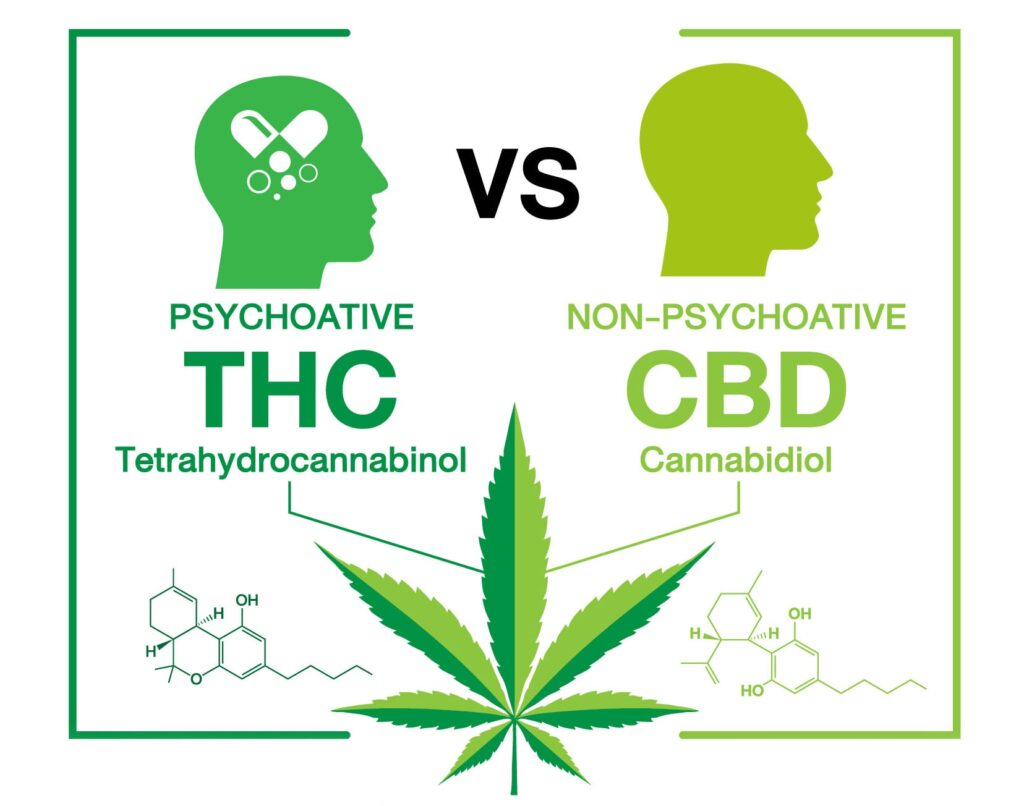
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines a psychoactive substance as one which, when ingested or administered, alters mental processes such as cognitive functions or affect.
CBD is one of many molecules derived from the hemp plant. Unlike THC*, it does not alter consciousness, in other words, it does not make you "high".
Cannabidiol is not only non-psychotropic, but also non-addictive.
Finally, again according to the WHO[1], CBD does not appear to have abuse potential, nor to be harmful to health.
As mentioned above, CBD is not addictive; on the contrary, it seems to have positive effects on addictions such as cannabis, alcohol, cigarettes and other drugs.
A 2018 clinical study[2] entitled "Treatment potential of cannabidiol for the prevention of relapse to drug use" first observed that CBD exerted relevant beneficial effects against several relapse-promoting conditions, such as sensitivity to drug- and stress-related contexts, anxiety and impaired impulse control.
A second study carried out in 2017[3] included a double-blind experiment, meaning that neither the researchers nor the participants knew what conditions they had been assigned to during the experiment.
Here, then, participants watched heroin-related videos and experienced high withdrawal effects. It was found that subjects who took CBD as part of the treatment showed fewer signs of craving than those in the placebo group after exposure to drug-related cues. The results also showed a reduction in anxiety, as well as a reduction in heart rate and cortisol, commonly known as the "stress hormone". CBD-related effects were visible as early as one hour after CBD administration and were still visible up to one week after the test.

According to a 2013 Dutch study[4],CBD can counteract the negative effects of THC. Cannabis strains with high levels of THC and low levels of CBD can cause increased psychiatric effects, such as paranoia, anxiety and addictive behavior.
A recent Canadian study[5](2019), administeredTHC to mice and on another sample both CBD and THC. The study found that the mice experienced anxiety and were receptive to fear-based learning. Subjects given both CBD and THC showed less anxiety and were less sensitive to fear-based learning.
Based on these results, the research team asserts that CBD blocks THC's ability to overstimulate the hippocampus (plays a central role in memory) and thus prevent its negative side effects.
A 2013 international study[6] also concludes along these lines, stating "Our main findings were that CBD inhibited THC-induced paranoia and inhibited THC's detrimental effects on episodic memory. In addition, CBD reduced the proportion of participants who experienced clinically significant acute THC psychosis."

CBD seems to have opposite effects on sleep, depending on the dose taken.
Two studies by Nicholson and Zuadi[7] et al have shown that a CBD dose of 160 mg/day increases sleep time in people suffering from insomnia. What's more, this high level may also help promote mental relaxation, which can reduce chronic stress and more pronounced anxiety symptoms.
Conversely, a lower dose, around 15 mg/day, has been shown to increase wakefulness in people suffering from insomnia. So at low doses, CBD can make you feel energized and alert, which can also help promote a state of calm and mental clarity.

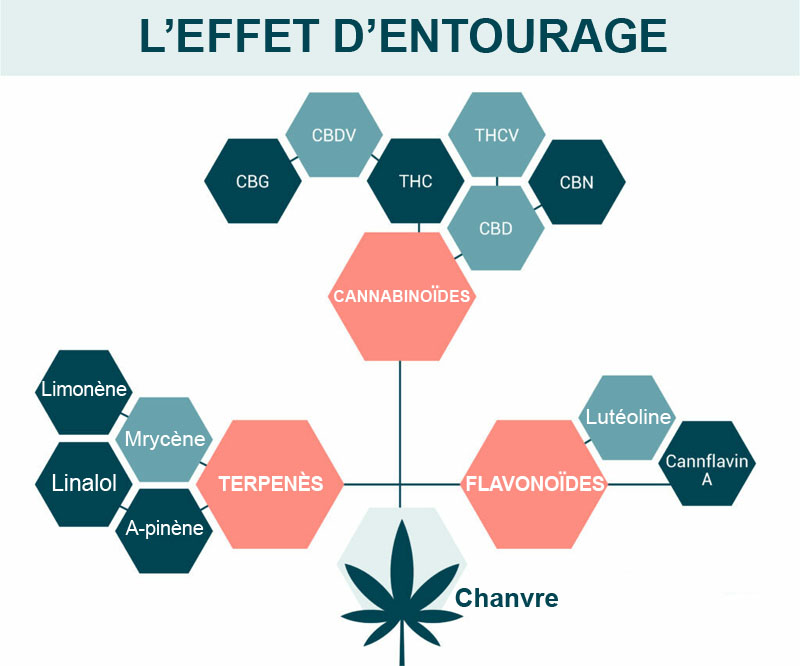
Perhaps you've already heard that CBD can improve the results obtained by practicing yoga or meditation? That's not all: according to several studies, including the 2015 study by the Hebrew University of Israel[8], when all the compounds in hemp are present(terpenes, cannabinoids: CBD, CBN, CBG, THC*, etc.), they act better together than they do in isolation.
The effectiveness of cannabinoids is enhanced when they are combined: this synergy is known as the "entourage effect".
For example, a high-end CBD flower like Jack Herer contains :
Could represent a natural ally in the case of depressive symptoms.
* THC is a prohibited substance in France (if levels exceed 0.2%).