Have a question? 06 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🔥 BIG DESTOCKING: EVERYTHING is on special 🔥
Have a question? 06 70 73 89 02

THCV, also known as tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a hemp-derived cannabinoid that had flourished in cbd shop after HHC was banned in June 2023.
Alongside its twin THCP and many others, THCV achieved a certain renown and was acclaimed by many consumers, before being banned in June 2024.
But for some time now, it has been making a comeback here and there in several CBD stores and CBD shop online. How does it work? What exactly is tetrahydrocannabivarin? What are its effects and what do we know about it? Here's a quick rundown of everything you need to know about THCV.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a minor cannabinoid naturally present in hemp and cannabis plants. Particularly in varieties whose genetics are derived from wild African hemp plants, such as the Durban Poison. We'll come back to this point in a moment.
At the molecular level, THCV is very similar to THC, with one exception: the side chain. THC has a pentyl carbon chain, with 5 atoms, whereas THCV has a propyl chain, with three carbon atoms. Incidentally, this is also the only difference with THCJD (Tetrahydrocannabioctyl), which has an octyl chain, with eight carbon atoms, and THCB (Tetrahydrocannabutyl) with a butyl chain with 4 carbon atoms.
This difference may seem minimal, but it radically changes the molecule's behavior and potency. In the case of THCV, the molecule interacts more lightly with the endocannabinoid system, making it less psychoactive than THC. It also has a shorter duration of action.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin was probably discovered and isolated for the first time in 1973, by a team of researchers led by the famous researcher Raphaël Mechoulam at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
The study focused on Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica varieties, particularly those from equatorial African regions, where the plants were known to produce unique cannabinoid profiles.
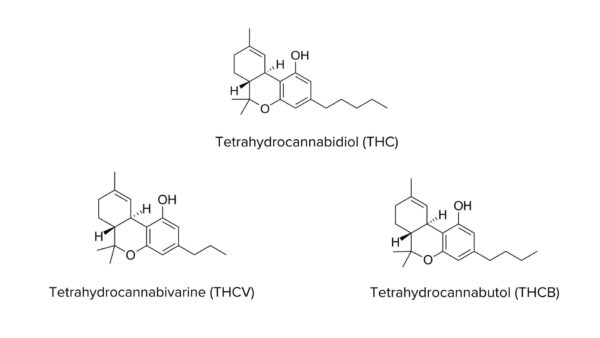
Thanks to this work, researchers have come to the conclusion that varieties indigenous to equatorial Africa, such as Malawi, Red Congolese, Power Plant and Jack the Ripper, have a fundamental difference from other varieties: their THCV content.
THCV levels don't usually exceed 0.5%, but on this type of variety they can reach 6% in dried flowers.
Fun fact: customs, port and police authorities then used the results of this study to determine whether the varieties seized originated in Central Africa by measuring THCV levels.
THCV has less psychoactive potential than THC, but its behavior is unique, especially when combined with THC. In low doses, it can limit the psychoactive effects of THC. But at high doses (over 2%), it has the opposite effect: it increases the effects of THC.
Among the other effects of THCV listed by the studies, the most important are:
Low-dose THCV has an antagonistic effect on CB1 receptors. This means it can help regulate feelings of hunger, particularly those associated with THC consumption[1].
Preliminary studies indicate that THCV may improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a potential candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[2].
THCV also exhibits neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, opening up prospects for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's. Studies suggest that THCV may protect dopaminergic neurons, but further research is needed to validate these effects[3].
A double-blind clinical study conducted by Phylos and People Science revealed that THCV can increase energy and motivation without causing the increased appetite often associated with THC. Participants who consumed THCV-infused candies reported an increased sense of energy and engagement in their daily activities[4].
In May 2024, the Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament (ANSM) decided to classify a large proportion of CBD-derived cannabinoids on the market as narcotics, prohibiting their production, sale and use in France from June 3, 2024. These included THCV, THCP, HHCPO and H3BN.
But this decision posed a problem for the hemp and cannabinoid industry, as the molecule is naturally present in most varieties. Its prohibition would have banned CBD, or organic hemp, at the same time.
Several organizations, including the Association Française des Producteurs de Cannabinoïdes (AFPC), the Union des Industriels pour la Valorisation des Extraits de Chanvre (UIVEC) and the Union des Professionnels du CBD (UPCBD), have pointed out that the total ban on THCV is excessive. The UPCBD even announced that it was preparing an appeal to challenge the classification of THCV as a narcotic.
In response to these statements, ANSM decided to reassess its position. On June 3, the day the ban came into force, it modified its initial announcement, excluding THCV from the list of narcotics, provided its content in products did not exceed 0.3%.
In short, THCV is not classified as a narcotic in France, but its concentration must not exceed 0.3%.
THCV is a very interesting new natural cannabinoid, both in terms of its potential applications and the complications it has encountered from a legal standpoint. In some respects, it is highly representative of the regulatory and medical challenges posed by new cannabinoids.
If you'd like to know more about the latest news on CBD and its derivatives, keep exploring our blog on the exciting world of CBD!